
The Solar Furnace
Working and its Applications
Introduction
A solar furnace is a device that concentrates and directs the sun's radiation to generate high temperatures, typically used for industrial processes such as melting and refining metals, producing high-temperature heat for power generation, or for scientific and experimental purposes. It usually consists of a large array of mirrors or lenses that track the sun and focus its light onto a central target area, creating intense heat. The technology is based on the principle of solar thermal energy and requires a clear, sun-rich environment to operate effectively.
Types of Solar Furnaces
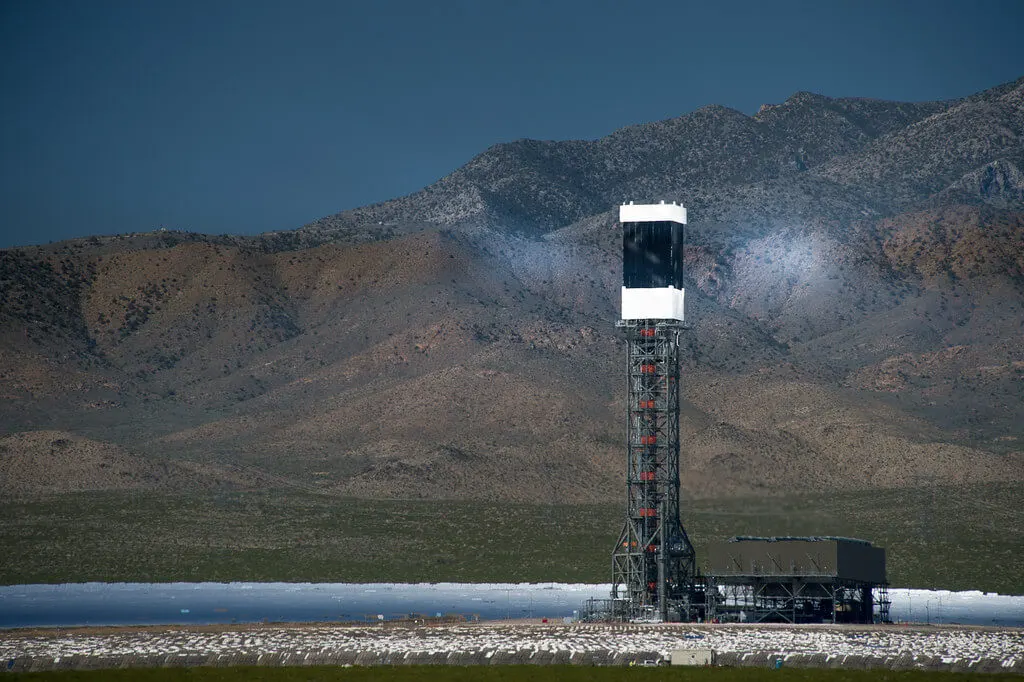
- Central Tower:
A central tower solar furnace uses a tall tower structure with an array of mirrors or heliostats that focus the sun's radiation onto a central receiver at the top of the tower. The central receiver absorbs the heat and transfers it to a heat exchanger or energy storage system. - Parabolic Trough:
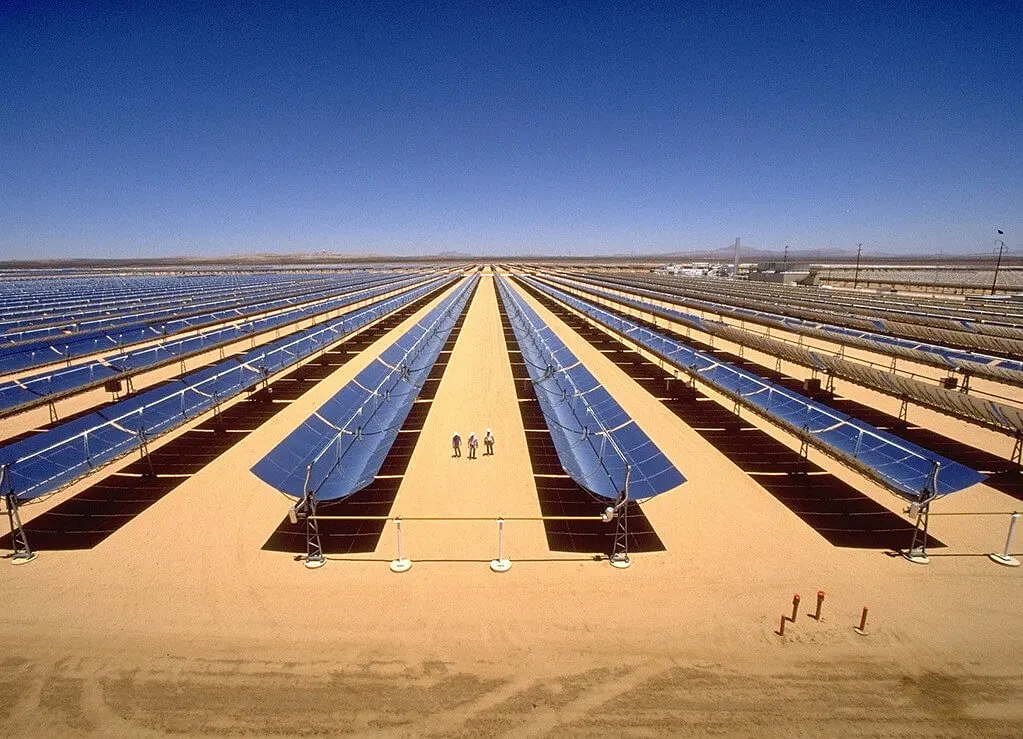
A parabolic trough solar furnace uses a series of parabolic mirrors or lenses that track the sun and focus its radiation onto a linear absorber located at the focus of the parabola. The absorber absorbs the heat and transfers it to a heat exchanger or energy storage system.

The Working
The basic working principle of a solar furnace is to concentrate and direct the sun's radiation to generate high temperatures.
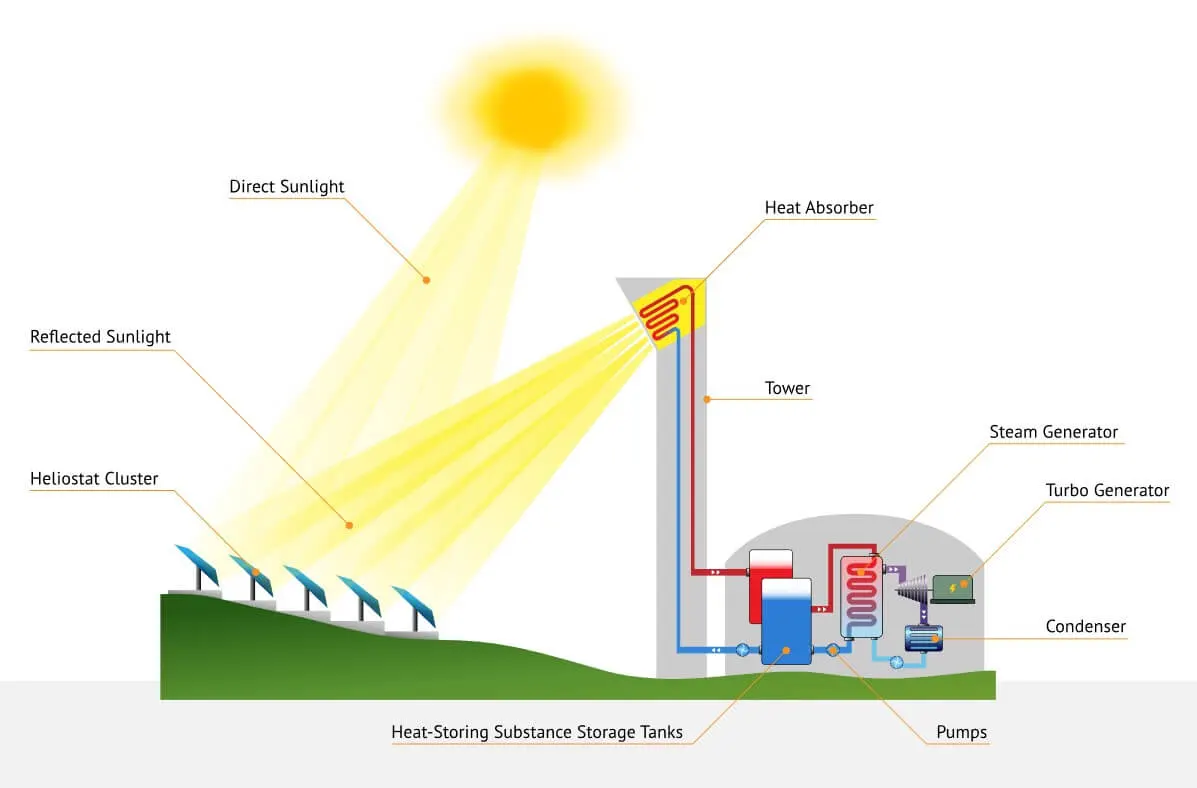
- Tracking the Sun:
The solar furnace consists of an array of mirrors or lenses that track the sun and adjust their angle to keep the sun's radiation focused on the target area. - Focusing the Sun's Radiation:
The mirrors or lenses focus the sun's radiation onto a central target area, creating a concentrated heat source. The size and number of mirrors or lenses determine the amount of heat that can be generated. - Absorbing the Heat:
The central target area, typically referred to as the absorber, absorbs the heat generated by the focused sun's radiation. This can be in the form of a receiver at the top of a central tower or a linear absorber located at the focus of a parabolic trough.
- Transferring the Heat:
The heat absorbed by the absorber is transferred to a heat exchanger or energy storage system, where it can be used for industrial processes, scientific experiments, or power generation. - Cooling the Absorber:
To prevent damage or degradation, the absorber must be cooled to maintain its integrity and efficiency. This can be done using a cooling fluid or other means, depending on the design and application of the solar furnace.
Key features
- High Temperature Generation:
Solar furnaces can generate extremely high temperatures, typically in the range of 1000-3000°C, making them ideal for industrial processes that require intense heat. - Renewable Energy:
Solar furnaces rely on renewable energy from the sun, making them a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional fossil fuel-based heating methods. - Concentrated Heat:
The focused light of the sun creates a concentrated heat source, making solar furnaces highly efficient in terms of energy utilization. - Versatility:
Solar furnaces can be used for a wide range of applications, including melting and refining metals, producing high-temperature heat for power generation, or for scientific and experimental purposes. - Cost-Effective:
Solar furnaces can be cost-effective in the long run, especially in regions with high levels of sunshine and low electricity costs. - Automated
Tracking: Solar furnaces typically come equipped with automated tracking systems that adjust the mirrors or lenses to keep the sun's radiation focused on the target area.

Solar Furnace : Pros & Cons
Pros of Solar Furnaces:
- Renewable Energy Source:
Solar furnaces rely on renewable energy from the sun, reducing dependence on finite and potentially harmful fossil fuels. - High Efficiency:
Solar furnaces are highly efficient in terms of energy utilization, as they concentrate and focus the sun's radiation to generate high temperatures. - Cost-Effective:
Solar furnaces can be cost-effective in the long run, especially in regions with high levels of sunshine and low electricity costs. - Environmentally Friendly:
Solar furnaces are a clean and sustainable alternative to traditional heating methods that generate pollutants and greenhouse gases. - Versatility:
Solar furnaces can be used for a wide range of industrial, scientific, and experimental purposes.
Cons of Solar Furnaces:
- Initial Cost:
The upfront cost of installing a solar furnace can be high, making it less accessible to some industries or regions. - Weather Dependence:
The performance of a solar furnace can be affected by weather conditions, such as cloudy days or stormy weather, limiting its usability in regions with low levels of sunshine. - Maintenance Costs:
The maintenance costs of a solar furnace can be high, as it requires regular cleaning and upkeep to ensure its efficiency. - Technical Expertise:
The operation and maintenance of a solar furnace require specialized technical knowledge, making it a more complex option compared to other heating methods. - Limited Applications:
The high temperatures generated by a solar furnace may not be suitable for some industrial processes, making it a more specialized option for certain industries.
Conclusion
Solar furnaces are a highly efficient and sustainable alternative to traditional heating methods that use renewable energy from the sun to generate high temperatures. With its versatility and cost-effectiveness in regions with high levels of sunshine, solar furnaces can be used for a wide range of industrial, scientific, and experimental purposes. However, the upfront cost and maintenance costs of a solar furnace, as well as its dependence on weather conditions and technical expertise, can limit its accessibility and usability. Nevertheless, as technology and design improve, solar furnaces hold the potential to play a significant role in reducing our dependence on fossil fuels and promoting a more sustainable future.