
Active vs. Passive Solar Systems: Key Differences Explained
Harnessing solar energy has become increasingly vital as the world shifts towards renewable energy sources. In this blog, we will explore two primary solar power systems—active and passive—and delve into their distinctions, advantages, and potential applications.
What Are Active and Passive Solar Power Systems?
Active and passive solar power systems represent two different approaches to harnessing the sun’s energy. Understanding their core differences can help you choose the most effective solution for your home or business.
Active Solar Power Systems use mechanical devices like pumps, fans, or photovoltaic (PV) panels to convert solar energy into usable power. On the other hand, passive solar power systems use architectural design to capture and distribute solar energy without the need for external devices.
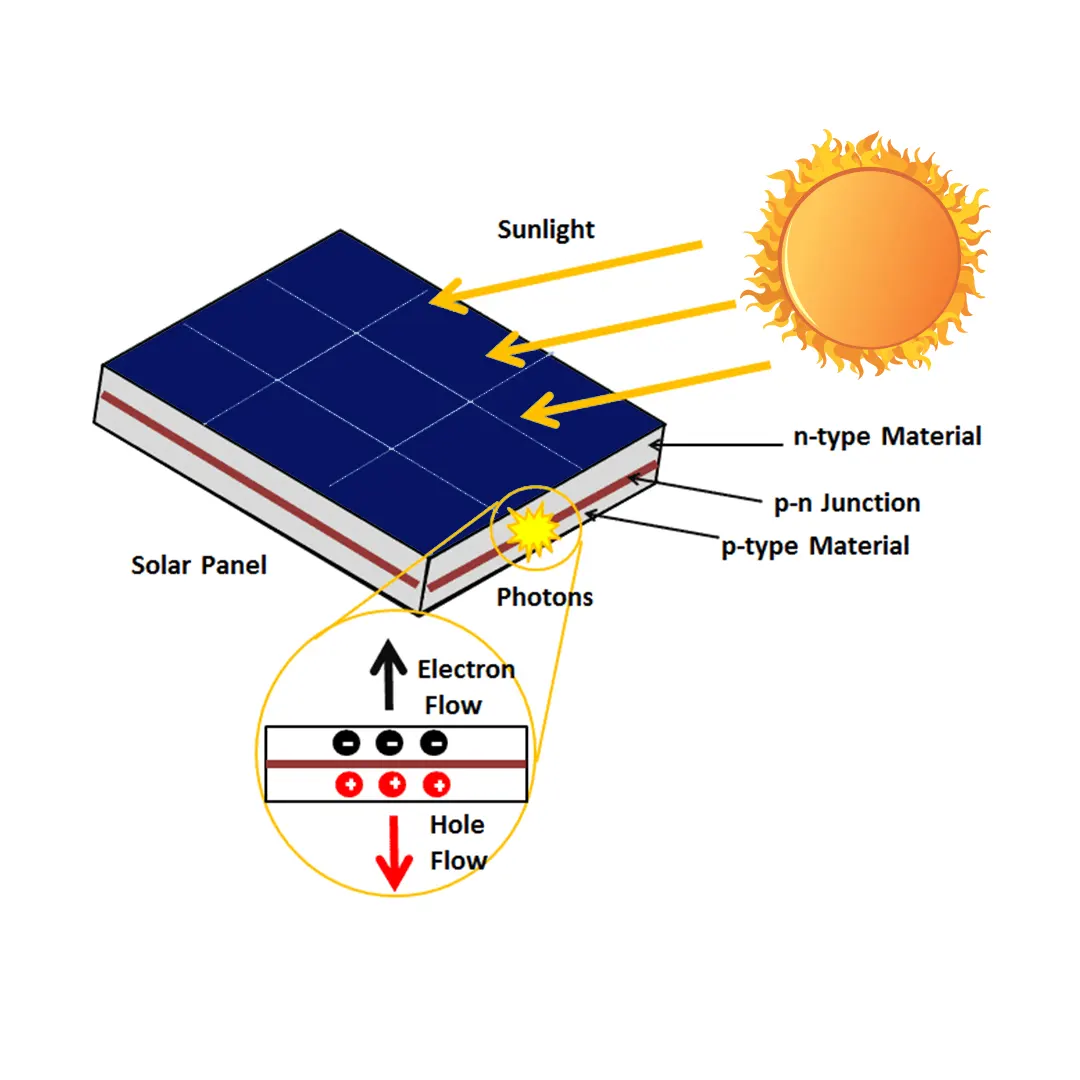
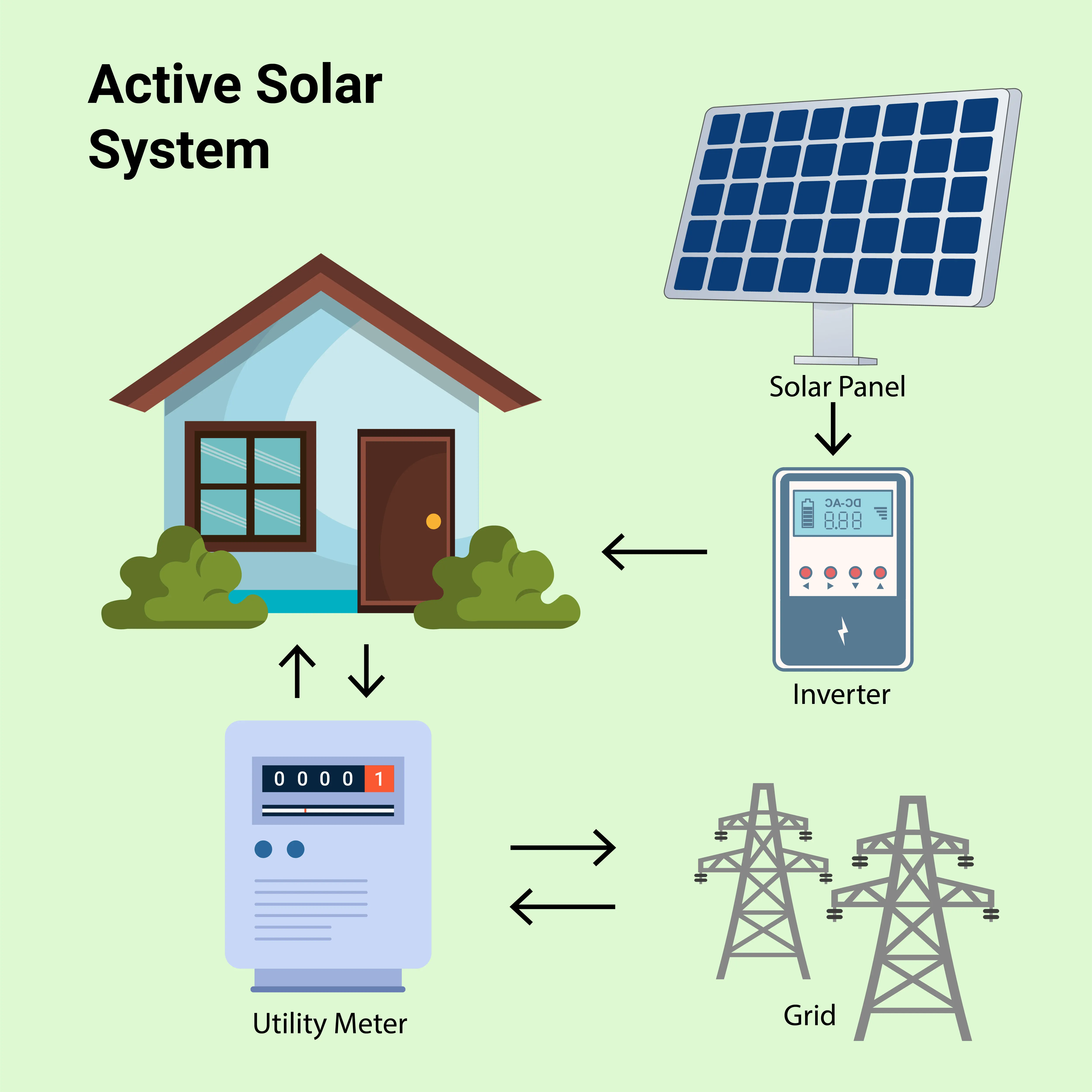
Active Solar Power Systems: How Do They Work?
Active solar systems are designed to absorb solar energy and convert it into electrical or thermal energy through photovoltaic panels or solar thermal collectors. These systems typically rely on a combination of solar modules and mechanical components to store and distribute energy.
Active solar energy systems work by using a fluid, such as air or liquid, to absorb heat from the sun. This heated fluid is then transferred to a storage unit, where it is eventually converted into usable energy. Unlike passive systems, active solar systems rely on external devices like solar panels to collect, store, and convert solar energy into power.
Liquids are often preferred due to their superior heat and energy conduction properties, but air has the advantage of not freezing in colder climates. Both air and liquid can be effectively used in heating or cooling a building. Liquid-based systems are known as hydronic collectors, while air-based systems are called air collectors.
Components of Active Solar Power Systems
Solar Panels: Active systems utilize monocrystalline solar panels and polycrystalline solar modules. These panels absorb sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC), which is then transformed into alternating current (AC) for home or business use.
Inverters and Batteries: These components help in storing excess energy and converting it for later use.
Solar Thermal Collectors: Active thermal systems capture sunlight to heat water or air for household needs.
Explore our top-quality solar panels.
Benefits of Active Solar Power Systems
Efficiency: Active systems can harness more energy due to their mechanical components.
Versatility: They are ideal for both residential and commercial applications.
Reliability: Active systems, when paired with energy storage solutions, offer a steady power supply.
By incorporating new solar panel technologies, active solar power systems continue to evolve and offer higher energy yields and greater reliability.
Passive Solar Power Systems: A Simpler Approach
Unlike active systems, passive solar power systems do not require any external devices to convert sunlight into energy. Instead, they rely on the architectural design of buildings to naturally absorb and store heat from the sun.
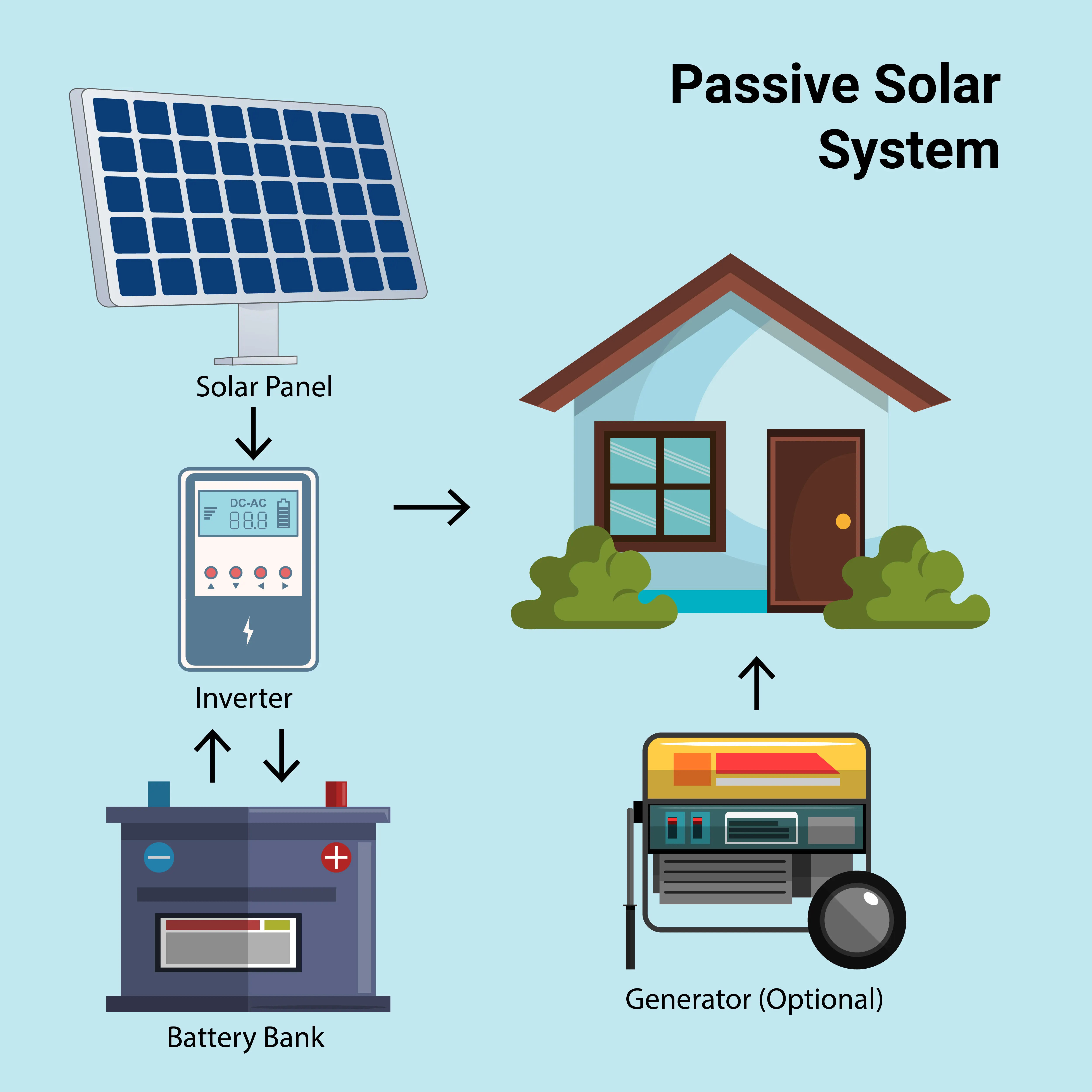
How Passive Solar Systems Work
Passive solar energy systems rely on the design, layout, and construction of a building to harness the sun’s energy, rather than using external devices. These systems naturally utilize sunlight for heating and cooling.
A common example is a car parked in the sun, where the metal body absorbs solar energy and heats the interior. This illustrates passive solar energy in action.
These systems work according to the laws of thermodynamics, where heat naturally transfers from warmer to cooler surfaces, helping to regulate indoor temperatures. Investing in passive solar systems for your small business is a smart choice since they operate without any external equipment, making them cost-effective and low-maintenance.
Explore more about Passive Solar Homes in our previous blog.
Key Elements of Passive Solar Power Systems
Aperture (Collector): The aperture is the part of a Passive Solar Heating system that allows sunlight to enter and be harnessed for energy. It can take the form of a window, skylight, or door. The size, shape, and placement of the aperture are key factors in determining how effectively the system captures and utilizes solar energy.
Thermal Mass: Materials like brick, stone, or concrete that absorb and slowly release heat.
The Heat Absorber: This refers to a solid, dark-colored surface—such as a masonry wall, floor, or water container—that is positioned to receive direct sunlight. Throughout the day, it absorbs heat and stores it in the 'thermal mass' behind, allowing the heat to be released gradually.
Natural Ventilation: Passive systems also rely on natural airflow to cool spaces.
Shading Devices: Overhangs or blinds help control the amount of sunlight entering the building during warmer months.
Benefits of Passive Solar Power Systems
A Renewable Energy Source : Passive Solar Heating is a clean and renewable energy source that generates no pollution or greenhouse gas emissions.
Cost-Effective: Since passive systems do not require complex technology, the initial costs are typically lower.
Low Maintenance: With no mechanical parts, passive systems are almost maintenance-free.
Eco-Friendly: Passive solar systems are ideal for those looking to reduce their carbon footprint.
Key Differences Between Active and Passive Solar Power Systems
While both systems serve the purpose of utilizing solar energy, they differ significantly in terms of components, cost, and functionality.
| Feature | Active Solar Systems | Passive Solar Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Generation | Uses photovoltaic panels and mechanical devices | Relies on architectural design |
| Cost | Higher initial costs due to technology and equipment | Lower initial costs due to simplicity |
| Efficiency | Highly efficient, especially in commercial applications | Less efficient, better for temperature regulation |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance of mechanical parts | Minimal maintenance required |
| Application | Suitable for electricity generation | Ideal for heating and cooling buildings |
Which System Is Right for You?
Choosing between active and passive solar systems depends on various factors such as your energy needs, budget, and the climate of your location.
Contact our solar energy experts today
The Future of Solar Energy: Advancements in Technology
As solar technology advances, both active and passive systems are becoming more efficient. New solar panel technologies such as bifacial panels and thin-film solar cells are paving the way for higher energy yields and lower costs.
Solar energy is also becoming more accessible and investing in cutting-edge technology, making it possible for more households and businesses to transition to renewable energy.
Explore more on our blog on latest innovations in solar panel technology.
Wrapping Up:
Both active and passive solar power systems offer significant benefits for harnessing solar energy. While active systems provide a higher energy output and flexibility, passive systems offer a cost-effective, low-maintenance solution for heating and cooling buildings.
Choosing the right system depends on your specific energy needs, location, and budget. Whether you opt for active solar design or a passive solar design, investing in solar energy is a step toward a more sustainable future.
Ready to make the switch to solar? Contact Us today to learn more about our products and services.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, active solar systems can still generate power on cloudy days, though the output will be lower than on sunny days.
Yes, passive solar systems can be designed to capture and retain heat even in colder climates.
With proper maintenance, active solar systems, including photovoltaic panels and inverters, can last 25 to 30 years.
Yes, many modern homes and buildings combine active and passive solar technologies to maximize energy efficiency.