Anti-Islanding in Solar Inverters: Ensuring Safety & Efficiency
When it comes to solar energy, efficiency and safety are crucial. Anti-islanding technology, a critical feature in modern solar inverters, plays a significant role in ensuring both. In this blog, we’ll delve into what anti-islanding is, why it matters, and how it operates in solar inverters to enhance the safety and reliability of solar energy systems .
What is Anti-Islanding in Solar Inverters?
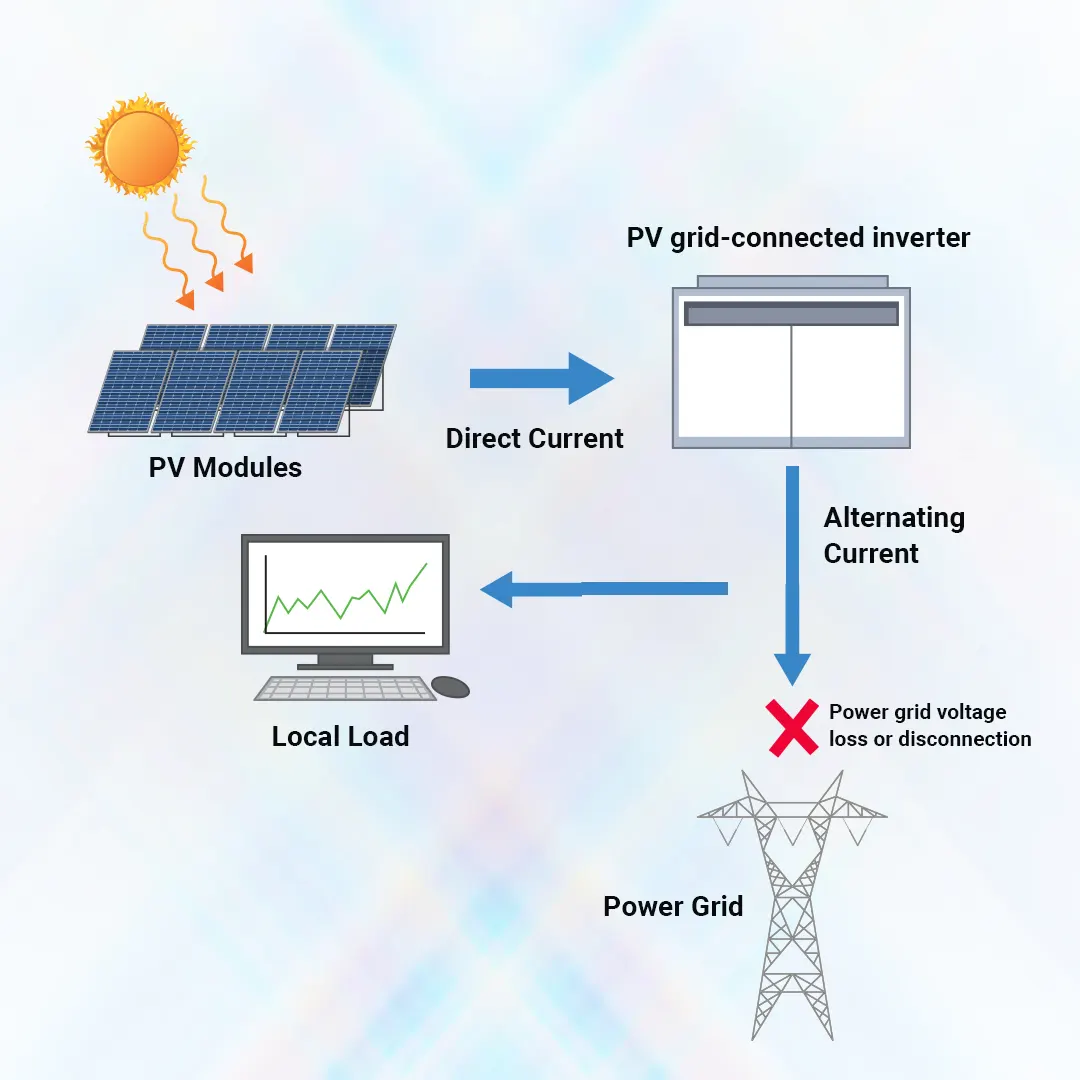
Anti-islanding is a safety mechanism designed to prevent a solar inverter from continuing to generate power when the main utility grid fails. Without this mechanism, solar inverters would continue to operate in an “islanded” mode, posing serious risks to utility workers, equipment, and the surrounding community. By implementing anti-islanding, solar inverters detect a grid failure and automatically disconnect, safeguarding both the system and the individuals involved.

Why is Anti-Islanding Important?
Implementing strong solar anti-islanding protection measures is crucial to protect the electrical grid’s stability and ensure the safety of workers. An islanded solar setup may continue to generate power during a grid outage if there are no trustworthy detection and disconnection procedures in place
When a grid outage occurs, the presence of an active solar inverter can create what’s known as an “island,” where the inverter continues to send power to the local network. This can cause two major issues:
Safety Risks: If utility workers believe that the grid is powered down, they may unknowingly encounter live electricity coming from a local solar inverter, putting them at serious risk.
Equipment Damage: Running solar power without grid synchronization can damage both the inverter and connected equipment.
Inverter damage: In large solar systems, multiple inverters are typically installed alongside distributed generators. Islanding can disrupt the inverters' proper functioning, potentially leading to damage.
How Does Anti-Islanding Work in Solar Inverters?
Anti-islanding technology in solar inverters operates through detection techniques designed to monitor and respond to the presence of the utility grid. Below are some common methods used:

Voltage Monitoring
Grid power loss can be detected using voltage monitoring, which involves continuously tracking grid voltage levels for significant drops or fluctuations. A sudden voltage decrease beyond a predefined threshold signals a grid outage or interruption. This activates the anti-islanding mechanism, ensuring disconnection from the grid to prioritize worker safety.
Frequency Monitoring
Frequency monitoring is a critical method for detecting power loss. By continuously tracking the power frequency, anti-islanding mechanisms can identify deviations from the normal range. During a grid outage, a lack of synchronization with other systems often causes noticeable frequency changes. The mechanism detects these variations and quickly disconnects from the grid, protecting inverters and other equipment from potential damage.
To ensure effective detection of islanding conditions in solar anti-islanding systems, a combination of active and passive methods is utilized. These methods assist in figuring out whether a photovoltaic (PV) system is still linked to the grid or has disconnected.
1. Passive Detection: Passive detection is the simplest method of anti-islanding. The inverter constantly monitors voltage and frequency; any significant fluctuations indicate a grid failure, prompting the inverter to disconnect immediately. However, passive detection alone may not always be effective.
2. Active Detection: Active detection is a more advanced approach, where the inverter injects small signals into the grid. When the grid is operational, these signals dissipate. However, during a grid failure, the inverter detects changes in the feedback, signaling it to shut down.
3. Hybrid Detection: A combination of passive and active detection, hybrid detection utilizes both methods to achieve more reliable anti-islanding. Hybrid systems are commonly used by solar panel manufacturers to enhance the inverter's response accuracy.
Components of an Anti-Islanding System
An anti-islanding system in a solar inverter relies on various components to ensure effective functionality. These include:
Monitoring Sensors: Continuously measure voltage, frequency, and phase.
Signal Injectors: Used in active detection to create test signals.
Control Unit: Decides when to disconnect the inverter based on detected grid conditions.
Using these components, solar module manufacturers in India ensure that anti-islanding systems are safe, efficient, and compliant with industry standards.
Benefits of Anti-Islanding in Solar Inverters:
Regular Maintenance and Testing: Routine maintenance and testing of anti-islanding protection systems are essential to ensure their reliability. Regular inspections allow solar system owners to detect and address potential issues or malfunctions in the anti-islanding mechanisms.
Enhanced Safety: Protects utility workers and prevents accidental electrocution.
System longevity: Guards against possible harm to the inverter and its associated equipment.
Compliance with Regulations: Many regions require anti-islanding features for grid-tied inverters.
Operational Efficiency: Reduces downtime and ensures synchronization with the grid upon reconnection.
Anti-islanding is a key component of solar inverters, ensuring that solar module manufacturers offer products that meet stringent safety requirements.
Types of Solar Inverters with Anti-Islanding:
Solar inverters equipped with anti-islanding technology fall into several categories:
1. Central Inverters: Central inverters are common in large-scale solar projects. They include robust anti-islanding systems to meet utility grid standards and are often used by photovoltaic panel manufacturers.
2. String Inverters: These inverters have effective anti-islanding measures and are often used by solar panel manufacturers in India for distributed installations.
3. Microinverters: Microinverters are attached to each solar panel, adding an additional layer of safety through built-in anti-islanding protection. This setup is ideal for smaller installations using polycrystalline solar modules and module mounting structures.
Interlinking Anti-Islanding with Other Solar Technologies
Anti-islanding is part of a broader set of technologies that solar manufacturers in India integrate to create efficient, reliable solar systems. In conjunction with advancements in solar module structure and materials, anti-islanding enhances the performance and safety of solar energy systems.
For those interested in learning more about the integration of anti-islanding with other solar technologies, check out our product page .
Wrapping Up
Anti-islanding is an essential feature in solar inverters, enhancing safety, ensuring compliance with regulations, and protecting both workers and equipment. As solar energy continues to expand in India, anti-islanding remains critical for the growth and reliability of distributed solar power.
Ready to make your solar system safer and more efficient?
Contact Us today to discuss solar solutions tailored to your needs!
By exploring advancements in solar technology, including anti-islanding, solar manufacturers in India are helping shape a cleaner, safer energy future. This blog covers not only how anti-islanding enhances safety but also how it fits into the broader landscape of renewable energy solutions, ensuring your solar investment is optimized and secure.
Frequently Asked Questions
Anti-islanding is a safety mechanism in solar inverters that automatically disconnects them from the grid during a power outage to prevent safety risks and equipment damage.
It ensures the safety of utility workers, protects equipment, and meets regulatory standards, enhancing the safety and efficiency of solar installations.
Anti-islanding systems use passive, active, or hybrid detection methods to monitor grid status and disconnect in the event of an outage.
Grid-tied solar systems without anti-islanding are often illegal due to safety risks, and most inverters today come with built-in anti-islanding features.