
Optimal Orientation for Solar Panels: Landscape vs. Portrait
Solar energy adoption is on the rise, with individuals and businesses increasingly investing in photovoltaic systems. However, a critical decision in solar panel installation often goes overlooked—the orientation of the panels. Whether to position panels in landscape or portrait orientation can significantly impact efficiency, installation feasibility, and overall energy yield. This blog explores the advantages, drawbacks, and best practices for selecting the optimal solar module orientation based on various factors.
Understanding Solar Panel Orientation
Before deciding on an orientation, it's essential to understand how solar panels function. A solar pv module converts sunlight into electricity through photovoltaic cells. The arrangement of these modules in an efficient solar module structure ensures maximum energy absorption. The placement and orientation of solar panels are as vital as their type. To maximize energy generation, panels must be positioned at the right angle and direction based on location and weather data. Optimal power is harnessed when sunlight hits perpendicularly.

What is Landscape Orientation
Landscape orientation, where solar panels are installed with their long side parallel to the ground, is a common and preferred choice due to its easy installation and compatibility with various mounting systems. It is often the default for solar designers, especially in commercial projects. However, while convenient, it may not always offer the best performance.
Advantages of Landscape Orientation
Ideal for Rooftop Installations: In residential settings, solar panels are often installed in a landscape orientation due to roof design constraints.
Lower Wind Resistance: Panels laid in a horizontal manner are less susceptible to wind uplift, making them more secure in high-wind regions.
Ease of Installation: Most solar module mounting structures are designed for landscape orientation, reducing the complexity of installation.
Secure Mounting with Rails: Landscape orientation aligns well with standard mounting rails, providing a stable and reliable foundation for solar panels.
Drawbacks of Landscape Orientation
Less Efficient in Certain Conditions: If space is limited, landscape panels may not optimize sunlight exposure compared to portrait setups.
Potential for Dirt Accumulation: Due to their horizontal nature, debris and dirt can accumulate more easily, requiring frequent cleaning.
What is Portrait Orientation
Portrait orientation involves installing solar panels with their long side vertically aligned to the ground. While previously less common, it has gained popularity due to its advantages in various applications.
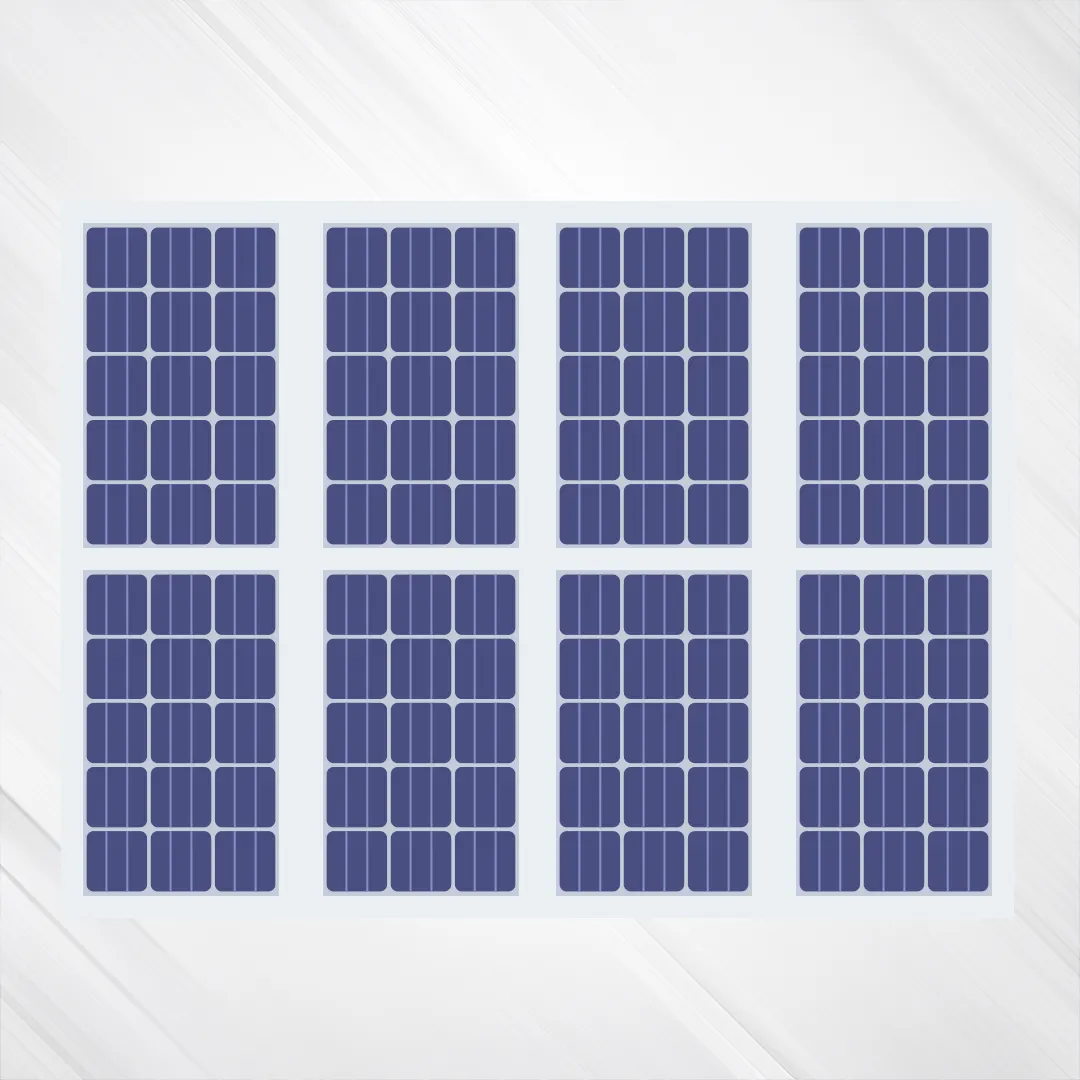

Advantages of Portrait Orientation
Higher Panel Density: More panels can be installed in portrait orientation in restricted spaces.
Improved Aesthetics: This orientation provides a cleaner, more uniform appearance, ensuring an unobstructed and visually appealing solar panel layout.
Enhanced Performance in Specific Conditions: In regions with high solar insolation, portrait orientation can improve energy generation by capturing more sunlight when the sun is at a lower angle.
Improved Aesthetics: This orientation provides a cleaner, more uniform appearance, ensuring an unobstructed and visually appealing solar panel layout.
Suited for Tracking Systems: Many modern solar energy manufacturer tracking systems favor portrait orientation for better performance.
Drawbacks of Portrait Orientation
Increased Wind Load: Panels positioned vertically are more exposed to wind forces, requiring stronger mounting solutions.
Limited Compatibility with Some Roofs: Residential rooftops may not always accommodate portrait setups effectively.

Factors Influencing the Best Orientation Choice
Choosing the right orientation for solar panels depends on multiple factors:
Geographical Considerations: The location of a solar installation plays a crucial role in determining the optimal panel orientation. In regions with varying sun angles throughout the day, portrait orientation may offer better solar exposure and efficiency.
Roof Space & Layout: For commercial buildings with expansive flat rooftops, landscape orientation is often preferred. However, homes with sloped roofs might benefit from a portrait layout to maximize available space.
Mounting Structures & Support Systems: A well-engineered solar module mounting structure ensures panel stability. Choosing the right support system, such as ground-mounted frames or tracking systems, influences orientation selection.
Solar Panel Efficiency: The efficiency of solar panels depends on their orientation and ability to generate electricity at different angles. While horizontal (landscape) panels may perform better in some cases, vertical (portrait) panels can be more effective in specific conditions.
Type of Solar Modules Used: The latest technology in solar panels impacts orientation choices. Some high-efficiency photovoltaic panels manufacturers offer bifacial panels that benefit from specific orientations to maximize energy generation from both sides.
Wind Load & Environmental Conditions: In regions prone to strong winds, landscape orientation might be preferred to minimize stress on mounting systems.
Wrapping Up
Choosing between landscape and portrait orientation for solar panels depends on numerous factors, including roof structure, mounting system compatibility, environmental conditions, and efficiency needs. Consulting with top solar module manufacturers and using advanced solar tracking tools can help make an informed decision. Whether installing for residential, commercial, or industrial use, selecting the right orientation is key to maximizing the benefits of solar energy.
Are you looking for expert guidance on selecting the right solar panel orientation for your project? Contact PIXON today for consultation and high-quality solar solutions.
FAQ Section
Yes, orientation plays a crucial role in how much sunlight the panels absorb, impacting overall efficiency.
It depends on roof layout and sun exposure. Landscape is ideal for wide, low-slope roofs, while portrait fits narrow, sloped roofs better.
Most solar panel manufacturers offer flexibility, but some high-efficiency models work better in specific setups.
Yes, hybrid setups are possible, especially in complex installations, but they require precise engineering.
The type of solar module mounting structures used determines the feasibility of landscape or portrait orientation.