Understanding the Key Components of a PV System
Renewable energy is becoming increasingly important today as we seek sustainable solutions to power our lives. Among the various forms of renewable energy, solar energy stands out for its efficiency, reliability, and environmental benefits. At the heart of solar energy systems are photovoltaic (PV) systems, which convert sunlight into electricity. This blog will provide an in-depth understanding of the key components of a PV system, explaining how they work together to harness solar energy effectively.
Overview of Solar PV Systems
A solar PV system consists of several components that work in unison to convert sunlight into usable electrical energy. These components include PV solar panels, solar modules, mounting structures, inverters, and various balance-of-system elements. Understanding each of these components is crucial for appreciating how a solar PV system operates and why it is a valuable investment for both residential and commercial applications.
How Photovoltaic Systems Work
Photovoltaic systems generate electricity by utilizing the photovoltaic effect, where semiconductor materials within solar cells absorb photons from sunlight and release electrons. This process creates an electric current that can be captured and used as electricity. The efficiency of this conversion process depends on the quality and type of solar cells used, as well as other factors like panel orientation and sunlight intensity.
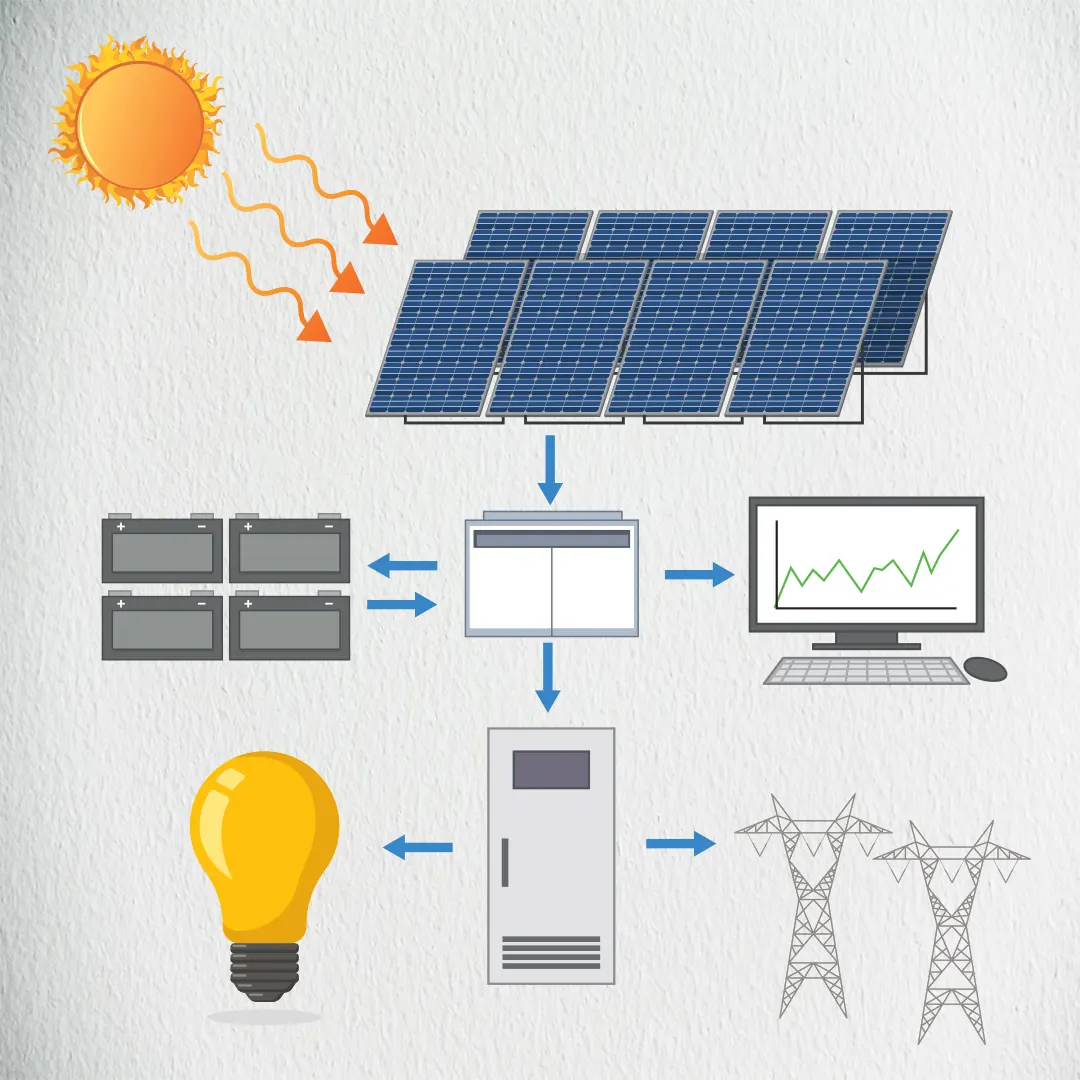
What are the Key Components of a PV System?
A comprehensive PV system includes several key components beyond the solar panels and inverters. These components include:
Solar Modules: The primary component that captures sunlight and converts it into electrical energy.
Inverters: Convert DC electricity from the solar panels into AC electricity for use in homes and businesses.
Mounting Structures: Securely hold the solar panels in place, ensuring optimal orientation and exposure to sunlight.
Battery Storage (Optional): Stores excess energy generated during the day for use during nighttime or cloudy periods.
Charge Controller: Regulates the flow of electricity to and from the battery storage, preventing overcharging and extending battery life.
Cabling and Wiring: Connects all the components, ensuring efficient and safe transfer of electricity.
Monitoring System: Tracks the performance of the PV system, providing real-time data and alerts for maintenance.
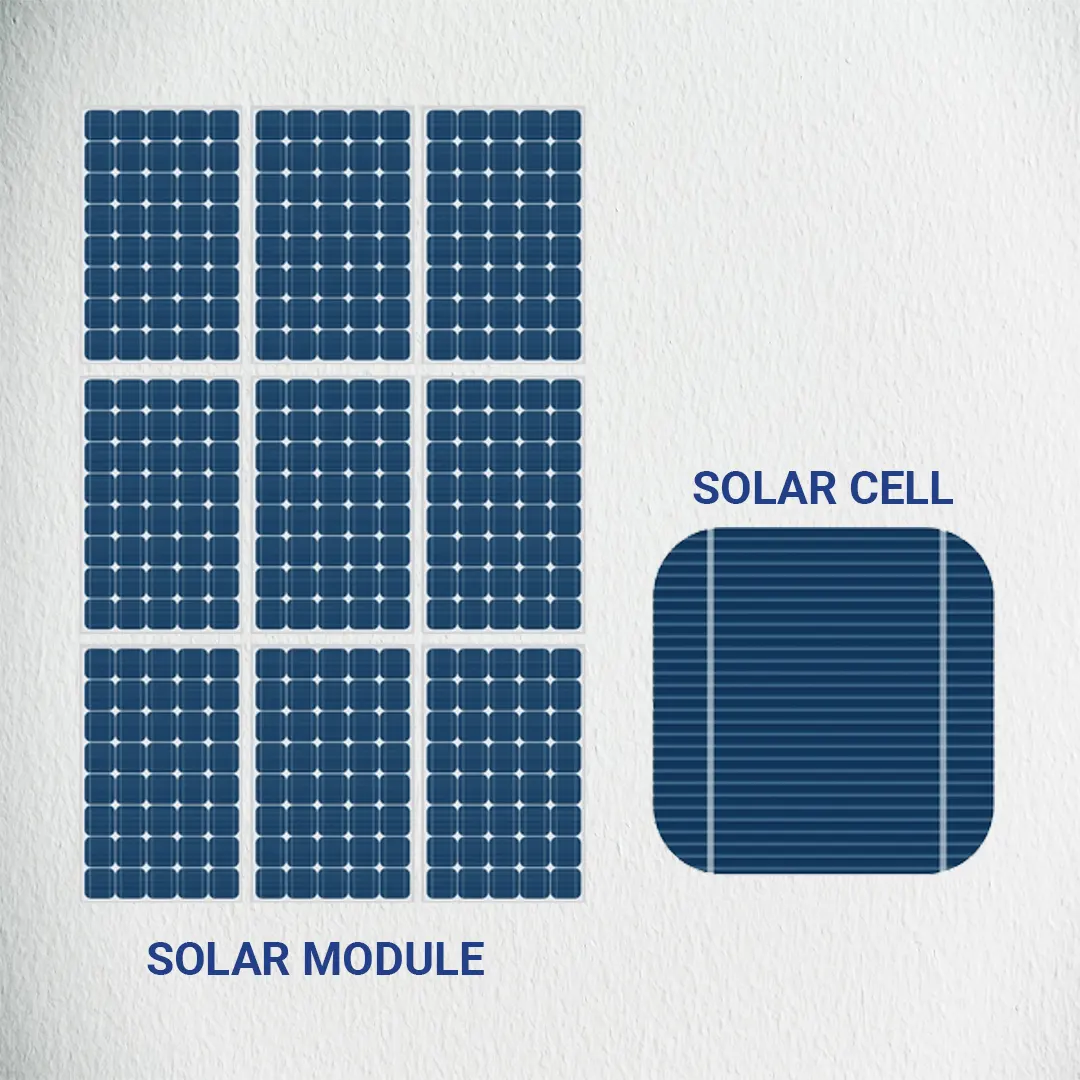
Solar Modules and Solar Cells
Solar modules, also known as solar panels, are the fundamental building blocks of a PV system. Each module consists of multiple solar cells connected in series or parallel to achieve the desired voltage and current output. A solar module's performance depends on its solar cells' efficiency and the quality of materials used in its construction.
PV solar panels come in various types, including monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film panels. Monocrystalline panels are known for their high efficiency and durability, while polycrystalline panels offer a cost-effective solution with slightly lower efficiency. Thin-film panels are flexible and lightweight, making them suitable for specific applications where weight and flexibility are critical factors.
Inverter
The inverter is a critical component of a PV system, responsible for converting the direct current (DC) generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC), which can be used to power household appliances and supply electricity to the grid.
Inverters come in different types, including string inverters, microinverters, and power optimizers, each offering unique benefits and suitability for various applications.
Module Mounting Structures
The effectiveness of a solar PV system heavily relies on the proper installation and orientation of the solar modules. This is where solar module mounting structures come into play. These structures support the solar panels, ensuring they are securely attached to the roof, ground, or other surfaces.
A robust solar module structure is essential for withstanding environmental factors like wind, rain, and snow. The structure must be designed to provide adequate support and stability while allowing for optimal sunlight exposure.
Solar module mounting structures come in various types, including fixed, adjustable, and tracking systems. Fixed mounting structures are stationary and set at a specific angle, while adjustable structures allow for manual changes in orientation to maximize sunlight capture.
Battery Storage
A battery storage enhances your self-consumption of solar energy and offers a dependable backup during grid outages. It stores excess energy produced by the PV array that isn't used right away. Including a battery storage in your solar PV system is optional
Charge Controller
Charge controllers manage the electricity from the DC generated by a solar array to charge a battery or a group of batteries. They regulate the voltage and current from the solar array to ensure the batteries are charged efficiently and safely.
Cabling and Wiring
It links all the components, ensuring the efficient and safe transfer of electricity.
Monitoring System
Tracking systems are more advanced, automatically adjusting the panels' position throughout the day to follow the sun's path and enhance energy production.
Types of Solar PV Systems
Solar PV systems can be categorized into three main types based on their configuration and usage:
Grid-Tied Systems: These systems are connected to the local electrical grid, allowing excess energy to be fed back into the grid and providing a reliable source of electricity when solar production is low.
Off-Grid Systems: These systems are independent of the grid and typically include battery storage to provide electricity during non-sunny periods. They are ideal for remote locations without access to the grid.
Hybrid Systems: Combining features of both grid-tied and off-grid systems, hybrid systems can switch between grid power and battery storage, offering greater flexibility and reliability.
Advantages of PV Systems
Solar PV systems offer numerous advantages, making them a popular choice for renewable energy solutions:
Environmental Benefits: Solar energy is a clean, renewable resource that reduces greenhouse gas emissions and decreases reliance on fossil fuels.
Cost Savings: Although the initial investment can be significant, solar PV systems can lead to substantial savings on electricity bills over time.
Energy Independence: By generating their electricity, homeowners and businesses can reduce their reliance on the grid and protect themselves from rising energy costs.
Low Maintenance: Solar PV systems have relatively low maintenance requirements, with most components designed to last for decades.
Increased Property Value: Installing a solar PV system can increase the value of a property, making it more attractive to potential buyers.

Wrapping Up
Understanding the key components of a PV system is essential for anyone considering investing in solar energy. From the solar modules and mounting structures to the inverters and additional system components, each part plays a crucial role in harnessing the sun's power and converting it into usable electricity. As a leading solar module manufacturer , PIXON offers a range of high-quality solar PV modules designed to maximize the efficiency and durability of your PV system. Explore more about our products and solutions at PIXON, and take the first step towards a sustainable and energy-efficient future.