Solar Panel Key Components: Exploring the Building Blocks of Solar Energy
Solar Inverters: Empowering Solar Energy Conversion for Homes and Businesses
Welcome to our latest technical newsletter- Solar Progress! In this edition, we will delve into the fascinating world of solar modules and explore the materials and components that make up these essential components of solar energy systems. So, let's uncover the secrets behind solar module construction!
Solar modules, also known as solar panels, are devices that convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. They are a key component of solar power systems and play a vital role in harnessing renewable energy. Understanding their composition will help us appreciate the engineering marvel behind solar energy generation.
-cells.webp)
Photovoltaic (PV) Cells:
At the heart of every solar module lies the photovoltaic cell, which is responsible for converting sunlight into electricity. PV cells are typically made of semiconductor materials, most commonly crystalline silicon. Silicon is abundant and possesses the necessary electrical properties to enable efficient energy conversion. Within the PV cell, the silicon is doped with impurities to create a positive and negative charge imbalance, facilitating the movement of electrons when sunlight interacts with the cell.
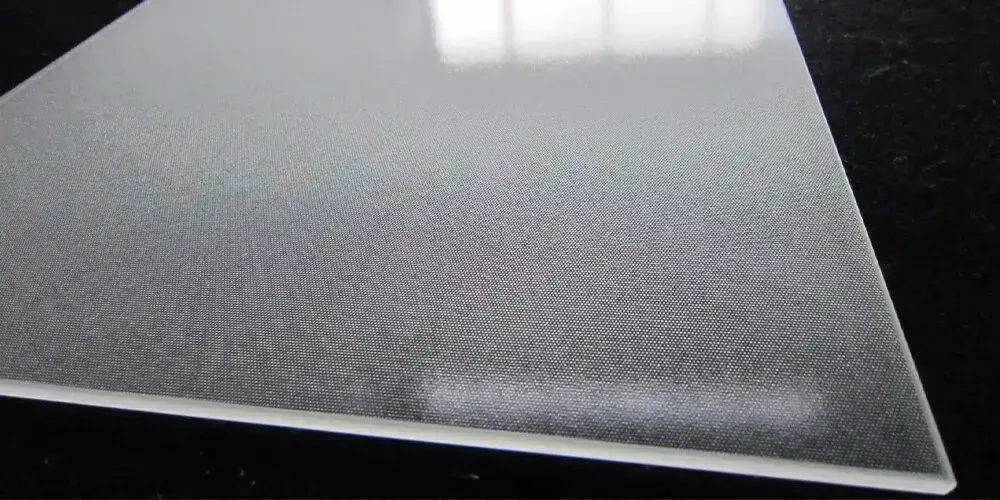
Highly Transparent Tempered Front Glass:
The front surface of a solar module is covered with a durable and transparent material, often tempered glass. This glass protects the PV cells from external elements, such as moisture and physical damage, while allowing sunlight to pass through

Encapsulant EVA Film and Insulating Backsheet:
To safeguard the delicate PV cells from environmental factors, a layer of encapsulant material is applied. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) is commonly used as an encapsulant due to its excellent light transmittance, adhesion properties, and resistance to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. The encapsulant also helps in providing electrical insulation.
The backsheet, located on the rear side of the module, acts as a barrier against moisture and provides electrical insulation. It is typically made of a polymer-based material, such as polyvinyl fluoride (PVF) or polyester.
Frame and Junction Box:
To support and protect the solar module, a frame is constructed around the edges. The frame is typically made of aluminum due to its lightweight nature, corrosion resistance, and structural strength.
The junction box, usually located on the rear side of the module, contains electrical components such as bypass diodes and wiring connections. It plays a crucial role in facilitating the interconnection of multiple solar modules to form an array and enables the efficient flow of electricity.

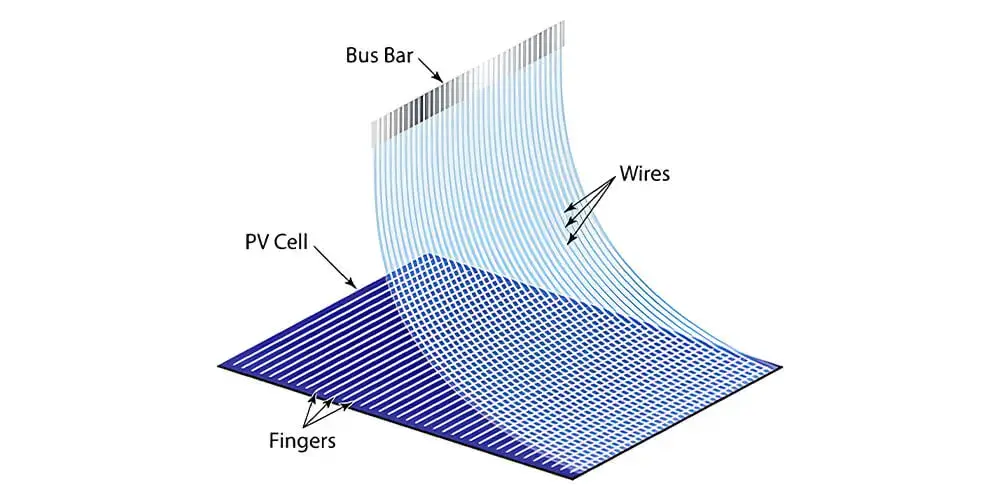
Interconnecting Wires:
Inside the module, interconnecting wires establish electrical connections between individual PV cells. These wires are designed to withstand environmental conditions and electrical currents generated by the cells.
By combining these components in a precise manner, solar module manufacturers create robust and efficient devices capable of harnessing sunlight to produce electricity.
It is worth noting that there are variations in solar module design and materials used across different technologies, such as monocrystalline silicon, polycrystalline silicon, and thin-film solar modules. Each technology has its own advantages and considerations when it comes to material composition and manufacturing processes.
Solar modules continue to evolve as researchers explore innovative materials and engineering techniques to enhance efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness. The ongoing advancements in the field promise a bright future for solar energy as a clean and sustainable power source.
We hope this newsletter has provided you with valuable insights into the composition of solar modules. As always, we encourage you to stay curious and keep exploring the ever-evolving world of renewable energy.