Understanding AC vs.DC Current in Solar Power Systems: What's the Difference?
In the world of solar energy, understanding the fundamental concepts of AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) is crucial. Whether you're a homeowner considering solar power for your residence, a business owner looking to reduce energy costs, or simply an enthusiast of renewable energy, grasping the differences between AC and DC currents is essential. This knowledge not only aids in making informed decisions but also enhances your appreciation of how solar PV modules work. In this newsletter, we'll delve into the intricacies of AC and DC currents, their applications in solar panels, and the advantages and disadvantages of each.
What are AC & DC Current?
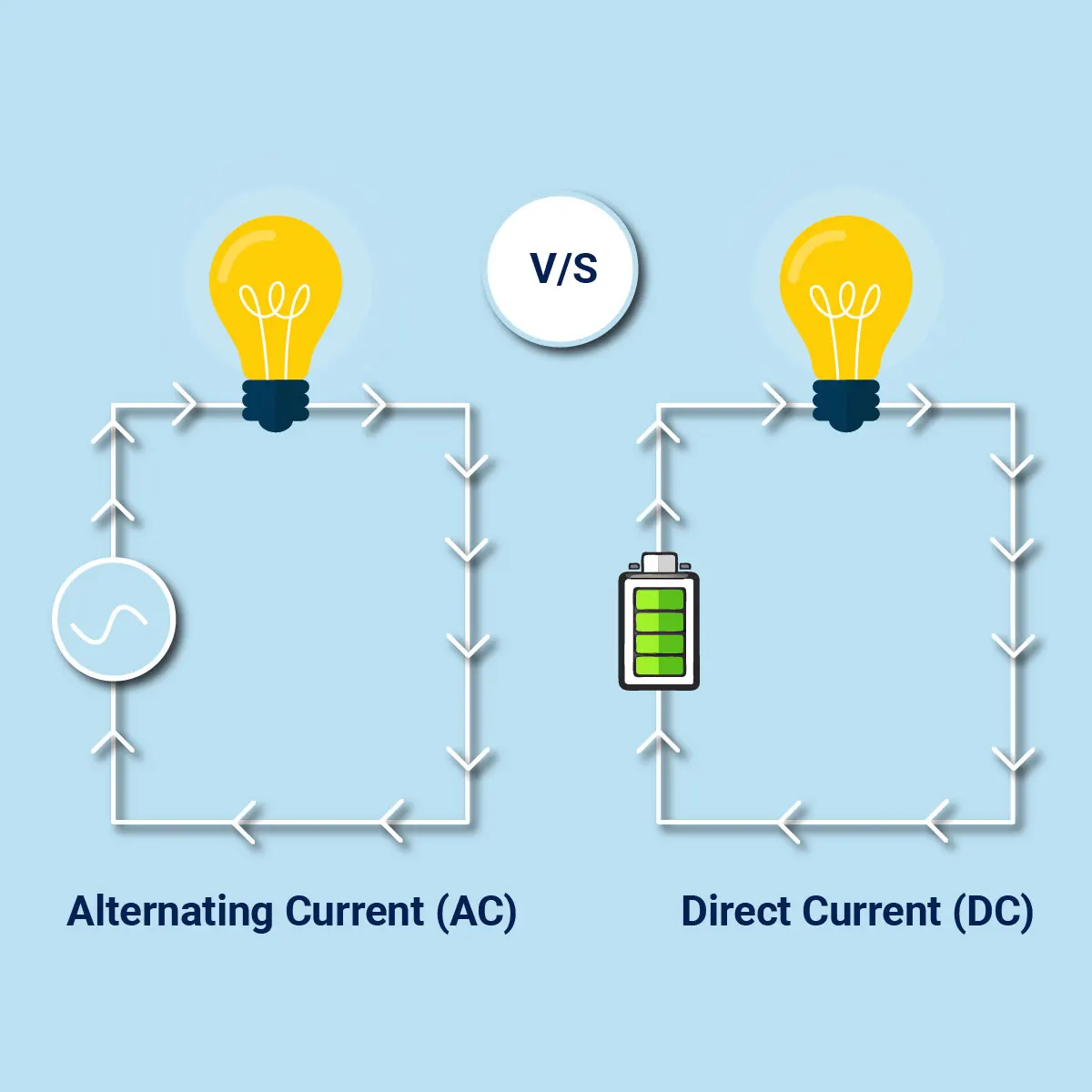
Direct Current (DC) is a type of electrical flow where the electric charge moves in a single direction. In DC, electrons travel from the negative side to the positive side of the power source, providing a consistent and steady stream of electricity. Batteries, solar cells, and fuel cells are common sources of DC electricity.
Alternating Current (AC) is characterized by the periodic reversal of its current flow direction. This means that the electrons move back and forth, changing direction at a frequency usually expressed in Hertz (Hz). The standard frequency varies by region, with 50 Hz being common in many parts of the world and 60 Hz in others. AC is the type of current typically supplied by power plants and used in homes and businesses due to its efficient transmission over long distances.
How are AC & DC used in Solar Panels?
The question of whether appliances use AC or DC power is common. The answer is that they use both. Solar panel batteries store energy as direct current (DC), which is then converted to alternating current (AC) for use in household appliances.
Solar panels generate electricity by capturing sunlight, which is stored as DC in batteries. This DC is then converted to AC by an inverter, making it usable for various AC-powered appliances. The primary function of solar panels is to convert captured DC energy into AC.
While solar panels generate DC, which can be used for battery storage and as backup power for devices, most household appliances require AC. Inverters play a crucial role in converting DC from solar panels into AC. The main difference between AC and DC solar panels is that AC panels have built-in inverters, providing AC directly at the output.
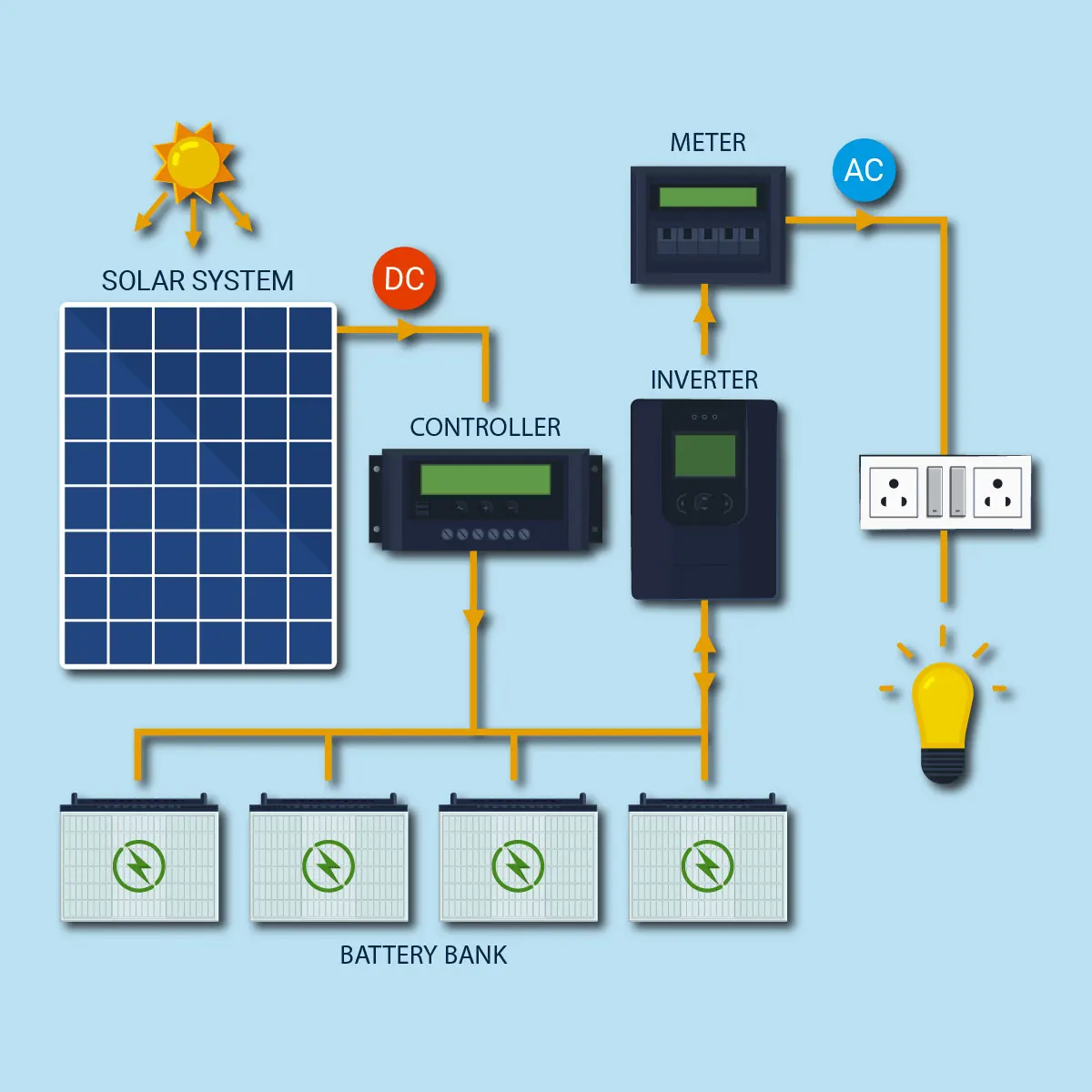
The process typically involves the following steps:
Generation: Solar panels absorb sunlight and generate DC electricity.
Conversion: The DC electricity is sent to an inverter, which converts it to AC.
Usage: The AC electricity is then used to power home appliances or sent to the grid.
Difference between AC & DC Current
The differences between AC and DC currents can be summarized as follows:
| Aspect | Alternating Current (AC) | Direct Current (DC) |
|---|---|---|
| Transmission Distance | Easily transferred over long distances, even between cities, with minimal energy loss. | Cannot be transferred over long distances without significant power loss. |
| Direction of Electric Flow | Rotating magnets cause the direction of electric flow to change. | Steady magnetism makes the current flow in a single direction. |
| Frequency | Dependent on the country, generally 50 Hz or 60 Hz. | No frequency or zero frequency. |
| Current Flow | Changes direction periodically (forward and backward). | Flows steadily in a single direction. |
| Electron Movement | Electrons change directions periodically (backward and forward). | Electrons move only in one direction (forward). |
Advantages and Disadvantages of AC & DC Current
Advantages of DC Current:
Stable and Consistent: Provides a steady stream of electricity, ideal for electronics and battery storage.
Efficient for Short Distances: Suitable for applications where power is needed over short distances.
Compatibility with Solar Panels: Directly generated by solar panels, reducing the initial need for conversion.
Disadvantages of DC Current:
Inefficiency in Long-Distance Transmission: Significant energy losses when transmitted over long distances.
Conversion Challenges: Voltage transformation is less efficient compared to AC.
Advantages of AC Current:
Efficient Long-Distance Transmission: Easily stepped up to high voltages, reducing energy loss during transmission.
Widespread Usage: Standard for household and industrial power supplies.
Versatility: Can power a wide range of appliances and devices.
Disadvantages of AC Current:
Complex Conversion Process: Requires inverters to convert from DC generated by solar panels.
Higher Risk of Shock: More dangerous due to the alternating nature of the current.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between AC and DC currents is fundamental to appreciating how solar power systems operate. DC current, generated by solar panels, must be converted to AC to be compatible with most home appliances and the power grid. Each type of current has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, influencing their applications in different scenarios.
As solar energy continues to grow in importance, solar PV module manufacturers like PIXON play a pivotal role in advancing technology and making solar power more accessible and efficient. For more information on innovative solutions in solar PV modules, visit PIXON.
By comprehending the distinctions between AC and DC currents, you are better equipped to make informed decisions regarding solar energy investments and installations. Whether it's for personal, commercial, or industrial use, understanding these basics ensures that you can fully harness the benefits of solar power.
In conclusion, both AC and DC currents are integral to the operation of solar power systems. The journey from sunlight to usable electricity involves both types of current, each contributing to the efficiency and functionality of solar energy solutions. As the world moves towards a more sustainable future, the role of solar manufacturers and top solar panel manufacturers in India , becomes increasingly significant in driving this change.
